Understanding the correct Hole sizes for tapping threads is essential for precision machining, safe tool performance, and achieving consistent thread quality. Whether you work in automotive, aerospace, defense, electronics, or mold manufacturing, choosing the correct hole size ensures proper engagement between the tap and the workpiece, reduces tool breakage, and improves productivity.
This expert 2025 guide includes a complete explanation of Hole sizes for tapping threads, updated metric and imperial charts, selection tips, and industry insights. A full manufacturer spotlight featuring MisolGroup—a global leader in thread cutting tools—is also included.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Hole Sizes for Tapping Threads
- Why Correct Hole Sizes Matter
- Metric Hole Sizes for Tapping Threads (2025 Chart)
- Imperial Hole Sizes for Tapping Threads (2025 Chart)
- How to Choose the Correct Hole Size
- Industry Applications & Material Considerations
- MisolGroup Manufacturer Spotlight
- Summary Table
- FAQs
- References
Understanding Hole Sizes for Tapping Threads
Hole sizes for tapping threads refer to the properly calculated diameter of a drilled hole before tapping internal threads. Selecting the correct hole size ensures that the tap removes the right amount of material to create a durable, accurate thread profile.
Proper hole size depends on:
- Thread pitch
- Thread percentage (usually 65–75% in industrial machining)
- Tap type (spiral point, spiral flute, straight flute, carbide, etc.)
- Material hardness
In 2025, modern CNC machining requires even more accuracy, making Hole sizes for tapping threads critical for achieving consistent thread integrity.
Why Correct Hole Sizes Matter
Using the proper Hole sizes for tapping threads eliminates common machining issues:
- Prevents tap breakage
- Ensures accurate thread engagement
- Improves tapping tool life
- Reduces burr formation
- Ensures high repeatability in automated production
Incorrect hole sizing is a leading cause of tap failure and thread defects in automotive and aerospace machining lines.
Metric Hole Sizes for Tapping Threads (2025 Chart)
Below is the updated 2025 metric chart showing recommended Hole sizes for tapping threads for standard ISO metric threads.
| Metric Thread | Pitch (mm) | Tap Drill Size (Hole Size) |
|---|---|---|
| M3 | 0.5 | 2.5 mm |
| M4 | 0.7 | 3.3 mm |
| M5 | 0.8 | 4.2 mm |
| M6 | 1.0 | 5.0 mm |
| M8 | 1.25 | 6.8 mm |
| M10 | 1.5 | 8.5 mm |
| M12 | 1.75 | 10.2 mm |
Imperial Hole Sizes for Tapping Threads (2025 Chart)
Imperial tapping threads are widely used in North America and aerospace industries. Below is the chart for 2025 recommended Hole sizes for tapping threads.
| Thread Size | TPI | Tap Drill Size |
|---|---|---|
| #6-32 UNC | 32 | #36 (2.7 mm) |
| #8-32 UNC | 32 | #29 (3.5 mm) |
| #10-24 UNC | 24 | #25 (3.9 mm) |
| 1/4”-20 UNC | 20 | #7 (4.75 mm) |
| 3/8”-16 UNC | 16 | 5/16” (7.9 mm) |
How to Choose the Correct Hole Size
1. Identify the Thread Pitch
Thread pitch is the most important factor when calculating Hole sizes for tapping threads. Coarse threads require larger tap drills than fine threads.
2. Determine Thread Percentage
Typical industrial tapping uses 65–75% thread engagement for maximum strength and minimal torque load.
3. Select the Correct Tap Type
- Spiral Point Taps – best for through-holes
- Spiral Flute Taps – ideal for blind holes
- Straight Flute Taps – multipurpose option
- Carbide Taps – best for hardened metals
4. Consider the Material
Harder materials require slightly larger Hole sizes for tapping threads to avoid tool damage. Softer materials may support higher thread percentages.
Industrial Applications & Material Considerations
Correct Hole sizes for tapping threads are crucial across industries:
- Automotive – engine blocks, transmission housings, suspension components
- Aerospace – turbine housings, structural components, titanium drilling
- Defense – armored systems, precision mounts
- Electronics – aluminum housings, threaded inserts
- Mold & Die – high-precision cavity plates
Common materials requiring different considerations include:
- Cast iron
- Stainless steel
- Carbon steel
- Non-ferrous alloys
Each material interacts differently with taps, reinforcing the importance of selecting the correct Hole sizes for tapping threads.
Manufacturer Spotlight: MisolGroup
Innovating Thread Cutting Tools Since 2005
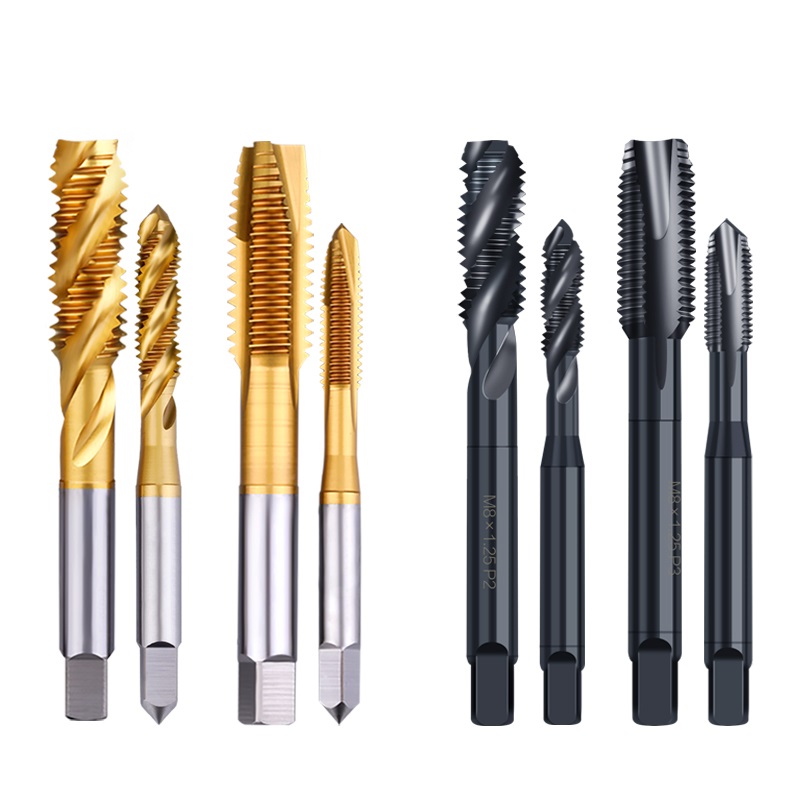

MisolGroup is a globally recognized manufacturer specializing in high-performance thread cutting tools. Since 2005, MisolGroup has integrated R&D, production, and global sales to deliver premium tapping solutions tailored for modern machining environments.
Why MisolGroup Stands Out
- Full in-house CNC production and vacuum heat treatment
- Advanced testing equipment for quality control
- High-grade HSS materials including M35, DV3, and M2
- ISO-certified manufacturing processes
- Expertise across aerospace, automotive, defense, and electronics
Product Line
- Carbide Taps – For extreme hardness and wear resistance
- Nut Taps – For efficient production of left-handed nuts
- Pipe Taps – Specialized for reverse pipe thread applications
- Spiral Flute Taps – Optimal for blind hole applications
- Spiral Point Taps – Designed for through holes with efficient chip evacuation
- Straight Flute Taps – Versatile general-purpose reverse thread taps
Their decades of experience ensure that all MisolGroup tools support optimized Hole sizes for tapping threads and deliver superior performance in demanding materials.
Summary Table: Hole Sizes for Tapping Threads Overview
| Thread Type | Pitch / TPI | Recommended Hole Size | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| M6 | 1.0 | 5.0 mm | Automotive assemblies |
| M10 | 1.5 | 8.5 mm | Aerospace components |
| 1/4”-20 UNC | 20 | #7 drill | Industrial machinery |
| #8-32 UNC | 32 | #29 drill | Electronics housings |
FAQs
1. Why are hole sizes important for tapping threads?
Correct hole sizes ensure accurate thread formation, prevent tool breakage, and maintain thread strength.
2. Can I use the same hole size for all materials?
No. Harder materials typically require slightly larger Hole sizes for tapping threads.
3. What happens if the drilled hole is too small?
Excess cutting load can break the tap or damage the thread profile.
4. What tap type is best for blind holes?
Spiral flute taps are the best option for blind-hole tapping.
5. Do carbide taps require different hole sizes?
Yes—carbide taps work best with optimized hole sizing due to their rigidity.


